The Nation’s Leader in Surplus, Seconds, Salvage, Opportunity & Spot Buys
Specializing in Short-Coded, Past “Best-Use-By” Dates and Discount Products
“Sustainability” — A Buzzword OR Something Truly Valuable?
As “environmental conservation” efforts continue to play a dominant role in a cultural conversation as well as a critical role in our nation’s “food supply” discussion, for consumers and those involved in the food industry, Marvell Foods is conscious of the role “food” plays” in our lives, beyond the obvious as food for sustenance.
“Sustainability” is also a directly related and critical consideration that businesses should be mindful of. As a food broker, buyer, and trader, Marvell Foods plays a contributing role in these ever-more-important issues by helping to minimize food waste (good for businesses – why destroy food when you can sell it – this approach is not only good for the bottom line – making it available through secondary outlets at discount prices – but, it is good during times of economic crises and food insecurity for millions of Americans – a situation the country has been dealing with since the beginning of the Corona Virus) whereas, Marvell Foods is a facilitator in this win-win paradigm – a scenario that is good for both business and consumers.
So, this discussion will address the following: A. what is the food system? More specifically, what is the current state of the food system? And B. To what extent does it contribute to environmental issues? Unfortunately, this system that once fueled urbanization supported a rapidly expanding population, and boosted economic development leaves the country and its citizenry in a dire situation. There’s a lot to question and consider, from food waste, surplus food, and the current industry norms that prioritize processed and unhealthy foods.
Consider the following about the types of food systems and how to improve food production for a more sustainable future.
How Does the Food System Work?
So, how does the food system work, and why does it not bode well for the future? While the current linear food system has sustained the demand of a growing population, it doesn’t come without high costs. Every dollar spent on food means that society pays two dollars in health, economic, and environmental costs, half of which come from the current food production processes. When it comes to the types of food systems, the linear implementation we see today extracts finite resources and harms natural systems by creating waste (often toxic, water waste, runoff and tainting underground water supply, local rivers, streams, lakes, etc.) while also developing as a by-product of food production – pollution – air and water. This linear system also relies heavily on intensive agricultural practices (contributing to Greenhouse Gas Effects and Climate Change) that place a demand on nearly 70% of global freshwater.
A food system diagram is perhaps the best way to showcase how this linear system operates. Below is an example of our current system. 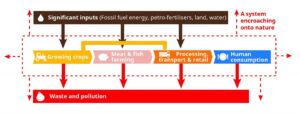
Source: https://feedbackglobal.org/building-better-food-system/
How to Improve Food Production
One of the first ways of understanding how to improve the food production system is by examining the actual cost of the current approach to food production. Food surplus and waste are certainly more significant contributors to the environmental consequences we face today, and this shows no sign of stopping unless specific measures are implemented. Some potential ways we can cut down on waste even in this linear path include:
- Sourcing food that is grown regeneratively
- Sourcing food locally when appropriate
- Creating healthier food products overall
- Making the most of food (particularly waste and surplus)
A linear food system indicates that the means of food production finitely end and reach an inevitable conclusion (waste). There is only so much we can do to reduce this waste, but the continual nature of this linear path means there will always be more. For this reason, conservationists have examined other food systems, such as circular ones that mimic natural regeneration systems. This way, waste does not exist but is the feedstock for another cycle—more on this below.
The Circular Food System Diagram
In a circular food system diagram, organic resources from food by-products are free from contaminants and can be safely returned to our soil as organic fertilizer. This cycle regenerates living systems and provides renewable resources while supporting biodiversity.
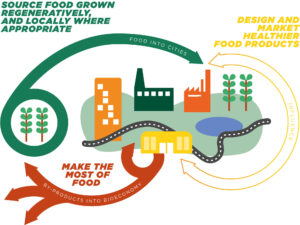
Source: https://archive.ellenmacarthurfoundation.org/explore/food-cities-the-circular-economy
The Role of Surplus Food Vendors
When considering how to improve food production and reduce waste, one should
consider the role of surplus vendors. These people, and companies, prioritize taking excess food such as meat, eggs, poultry, fruits & boxed/canned goods that would otherwise go to waste and find ways to redistribute them. Sometimes this can be through volunteer efforts such as food drives, other times, it can be through surplus food markets, where goods are close to their expiration date but still wholly viable for consumption.
Often, retailers get nervous about Close-Coded foods on their shelves and seek to clear this inventory. Marvell Foods is a big buyer of this type of (food product(s)) and offers these perfectly wholesome goods to its nationwide client base of discount stores, food banks, and a host of other unique buyers Marvell Foods has cultivated over many years in the food business. Expired Foods suffer a similar fate when retailers want to quickly dispose of these goods, which, fortunately, still have a valuable afterlife in the secondary market. Once again, Marvell Foods is not only a buyer of these goods, but Marvell Foods is also a direct buyer of these goods because it has a network of buyers who will purchase these products. Last ditch efforts to recoup capital on expired or soon-to-be expired foods, Marvell Foods also has outlets with Pet Food Ingredient companies. The bottom line, there is always somewhere to go with close-coded or expired food items while being able to generate revenue on an otherwise potentially unsellable product.
The Food System of the Future
So, what is the food system of the future? Will it involve a complete process overhaul, or will it remain the same as external sources, vendors, producers, and even consumers work to counter the ill effects of surplus food? While these various strategies and systems compete for such a title, the future food system should ultimately change the current industry landscape for the better, turning it into a more sustainable, functional, and cost-effective system that benefits everyone.

